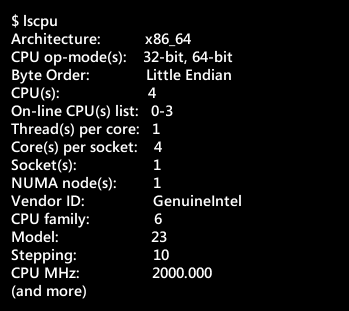
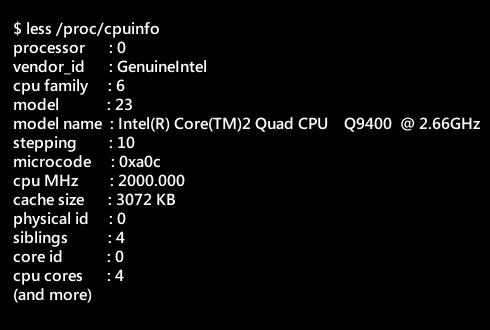
Don’t let Windows or Mac users scare you that adding or removing software on a Linux computer is only for bravehearts.
Installing, upgrading or removing software on Linux systems is no longer the daunting chore it used to be some years back.
Broadly speaking, there are two ways to install software packages on a Linux system.
You can install software packages either through a graphical user interface (GUI) or do it via the command line.
Major desktop Linux distros like Fedora Workstation 21, Linux Mint and Ubuntu now have slick GUIs that make searching for and installing new software a breeze.
The big advantage with GUI based installers is that they take care of dependency resolution so newbies won’t have to fret whether the package they’re installing or upgrading will work without having to install other software.
But you can be sure that hardcore Linux enthusiasts and system administrators will always opt for the command line to install, upgrade or remove software.
In large business environments (such as a web hosting companies) where headless servers are often the norm, Linux system administrators work exclusively on the command line.
Command Line Installation
On the command line, two kinds of tools (low level and high level) are available to install software packages on a Linux system.
The first method (dpkg for Debian and rpm for Red Hat) does not resolve dependencies and are therefore considered low level tools.
The high level installation tools (apt-get or yum) take care of dependencies.
In case you didn’t know, dependencies are other software that an application requires before it can work.
dpkg and rpm are low-level tools while apt-get and yum are considered high-level tools because they take care of dependencies as part of the installation process.
In this post, we’ll look at installing and removing software packages on both Debian based distributions and Red Hat style distros (like Fedora, CentOS and OpenSUSE that follow the Red Hat methodology) via the command line.
As you no doubt guessed, the commands for Debian and Red hat are completely different.
So we’ll have to consider them separately to avoid confusion.
We’ll consider Debian and its derivative distros first.
Installation on Debian
Commands mentioned in this section should work on Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Xandros and more.
Install a Package
Linux users opt for dpkg with software that are not downloaded from a repository.
Here’s how you install a package with dpkg.
# dpkg -i package_name
When you install a .deb package via the low-level dpkg tool, be aware that there is no dependency resolution.
So if the package you’re installing requires other software you’re stuck.
To avoid dependency issues, you must use higher-level tools like apt-get to install software on Debian and its derivatives. Strictly speaking, this is not always possible because not all packages are in repositories.
When you use the high level apt-get install tool, you’re downloading software from a repository.
The first step is to run update and then search for the package you’re interested in.
# apt-get update
# apt-cache search search_string
If you’re looking for an RSS reader, you’d run the below command first.
# apt-cache search rss
That’s how I discovered RSS readers like Quiterss and Liferea.
Finally, when you’ve found the package you want just install it with the following command.
You can skip the search step if you already know the package you want to install.
# apt-get install package_name
List Packages Installed
Your Ubuntu or Linux Mint computer has dozens of packages installed on it.
If you want the entire lengthy list, go with the following command.
$ dpkg -l
I recommend you save the output to a text file for leisurely analysis later.
$ dpkg -l > MyPackageList.txt
Total Packages Installed
Say you want to find out how many packages are installed on a Linux system without the long list of all the individual packages.
You use the dpkg with the -l option and then pipe it to wc -l.
On my Ubuntu system, I was curious about the total packages installed.
Here’s what I did:
$ dpkg -l | wc -l
2215
Remove a Package
Removing a package on a Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint computer is no sweat with the below command.
# dpkg -r package_name
Alternatively, if it’s a package downloaded from a repository you should go with either of the following commands.
# apt-cache remove package_name
But the above command leaves behind configuration files.
If your goal is to remove the configuration files too, you must use the purge option.
apt-cache purge package_name
Information About a Specific Package
If you’re looking for more information on a specific package, what command would you run?
In the below example, I sought information on the popular Cherrytree notes application.
$ dpkg -l cherrytree | tail -1 | tr -s ' '
ii cherrytree 0.35.7-1~ppa1~trusty1 all hierarchical note taking application
Verify if Package is Installed
You can check if a particular software package is installed on your Debian or Ubuntu computer.
Say you want to see if an rss package is installed on your Ubuntu computer.
Here’s the command you ought to run:
$ dpkg -l | grep rss
ii quiterss 0.17.6-0ubuntu1~trusty amd64 RSS/Atom feed reader written on Qt
If quiterss weren’t installed on my Ubuntu PC, I wouldn’t have got any response.
Red Hat & Red Hat Syle Distros
Let’s now take a dekko at how to install software on Red Hat and its derivative distributions like CentOS and Fedora.
Red Hat is the favorite Linux distro for scores of large corporations around the world. Continue reading »
 Learning how to do a clean shut down of a Linux system is important if you don’t want to mess up your computer.
Learning how to do a clean shut down of a Linux system is important if you don’t want to mess up your computer.

 The command line interface is so versatile that you can find considerable information about even the hardware side of your Linux server or desktop.
The command line interface is so versatile that you can find considerable information about even the hardware side of your Linux server or desktop.